Bluetooth - Bluetooth
 | |
| Tomonidan ishlab chiqilgan | Bluetooth maxsus foizlar guruhi |
|---|---|
| Tanishtirdi | 1989 yil 7-may |
| Sanoat | Shaxsiy tarmoq tarmoqlari |
| Mos keluvchi apparat | Shaxsiy kompyuterlar Smartfonlar O'yin pristavkalari Ovoz qurilmalari |
| Jismoniy diapazon | Odatda 10 m dan kam (33 fut), 100 m gacha (330 fut) Bluetooth 5.0: 40-400 m (100-1000 fut)[1][2] |
Bluetooth a simsiz Qisqa masofalarda qattiq va mobil qurilmalar o'rtasida ma'lumot almashish uchun ishlatiladigan texnologiya standarti UHF radio to'lqinlari ichida sanoat, ilmiy va tibbiy radiostansiyalar, 2,402 gigagertsdan 2,480 gacha GHz va bino shaxsiy tarmoq tarmoqlari (PAN-lar). Dastlab u simsiz alternativ sifatida ishlab chiqilgan RS-232 ma'lumotlar kabellari.
Bluetooth boshqariladi Bluetooth maxsus foizlar guruhi (SIG) telekommunikatsiya, hisoblash, tarmoq va maishiy elektronika sohalarida 35000 dan ortiq a'zo kompaniyalarga ega. The IEEE sifatida standartlashtirilgan Bluetooth IEEE 802.15.1, lekin endi standartni saqlamaydi. Bluetooth SIG spetsifikatsiyani ishlab chiqishni nazorat qiladi, malaka dasturini boshqaradi va savdo belgilarini himoya qiladi.[3] Ishlab chiqaruvchi uchrashishi kerak Bluetooth SIG standartlari uni Bluetooth qurilmasi sifatida sotish uchun.[4] Tarmoq patentlar individual malakali qurilmalar uchun litsenziyalangan texnologiyaga amal qilish. 2009 yildan boshlab[yangilash], Bluetooth integral mikrosxema chiplar taxminan 920 donani etkazib beradi har yili million dona.[5]
Etimologiya
"Bluetooth" nomi 1997 yilda Jim Kardach tomonidan taklif qilingan Intel, mobil telefonlarning kompyuterlar bilan aloqa qilishiga imkon beradigan tizimni ishlab chiqqan.[6] Ushbu taklif paytida u o'qiyotgan edi Frans G. Bengtsson tarixiy roman Uzoq kemalar Vikinglar va 10-asr Daniya qiroli haqida Harald Bluetooth.[7][8]
Bluetooth Angliya qilingan Skandinaviya versiyasi Blatand/Blatan (yoki in.) Qadimgi Norse blátǫnn). Bu edi epitet Daniyalik kelishmovchilik qabilalarini yagona qirollikka birlashtirgan qirol Xarald Bluetooth, natijada Bluetooth aloqa protokollarini birlashtiradi.[9]
Logotip
Bluetooth logotipi ![]() a Runi bog'lash birlashtirish Yosh Futhark runlar
a Runi bog'lash birlashtirish Yosh Futhark runlar ![]() (ᚼ, Xagall ) va
(ᚼ, Xagall ) va ![]() (ᛒ, Byarkan ), Haraldning bosh harflari.[10][11]
(ᛒ, Byarkan ), Haraldning bosh harflari.[10][11]
Tarix
Keyinchalik "Bluetooth" deb nomlangan "qisqa aloqali" radiotexnologiyani rivojlantirish 1989 yilda CTO da Nils Rydbek tomonidan boshlangan. Ericsson Mobile yilda Lund, Shvetsiya. Maqsad Yoxan Ullmanning ikkita ixtirosiga ko'ra simsiz eshitish vositalarini ishlab chiqish edi, SE 8902098-6, 1989-06-12 yillarda chiqarilgan va SE 9202239, 1992-07-24 da chiqarilgan. Nils Raydbek Tord Vingrenga aniqlik kiritish va gollandiyalikni topshirdi Yaap Haartsen va Sven Mattisson rivojlanmoqda. Ikkalasi ham Lunddagi Ericssonda ishlagan.[12]1990 yilda Yaap Haartsen Evropa Patent idorasi tomonidan Evropa ixtirochilar mukofotiga nomzod qilingan. [13] 1997 yildan Örjan Yoxansson loyihaning etakchisiga aylandi va texnologiya va standartlashtirishni ilgari surdi.[14][15][16][17]
1997 yilda Adalio Sanches, o'sha paytda IBM ThinkPad mahsulotining Ar-ge bo'yicha rahbari bo'lib, Nils Raydbekga dasturni birlashtirish bo'yicha hamkorlik qilish to'g'risida murojaat qildi. Mobil telefon ThinkPad daftariga. G'oyani o'rganish uchun Ericsson va IBM kompaniyalaridan ikkita muhandis tayinlangan. Xulosa shundan iboratki, o'sha paytdagi uyali telefonlar texnologiyasida quvvat sarfi juda yuqori bo'lib, noutbukga hayotiy integratsiyani va shu bilan birga batareyaning ishlash muddatini ta'minlashga imkon bermadi. Buning o'rniga, ikkita kompaniya maqsadni amalga oshirish uchun Ericsson-ning qisqa ulanish texnologiyasini ham ThinkPad daftariga, ham Ericsson telefoniga qo'shishga kelishib oldilar. O'sha paytda na IBM ThinkPad noutbuklari, na Ericsson telefonlari o'z bozorlarida bozor ulushi etakchisi bo'lmagani uchun Adalio Sanches va Nils Raydbeklar har bir o'yinchiga bozorga maksimal darajada kirish uchun ruxsat beruvchi qisqa aloqa texnologiyasini ochiq sanoat standartiga aylantirishga kelishib oldilar. Ericsson qisqa aloqali radiotexnologiyani va IBM mantiqiy qatlam atrofida patentlarni taqdim etdi. Keyinchalik IBM xodimi Adalio Sanches Intel kompaniyasidan Stiven Nachtsxaymni o'z safiga qo'shib oldi, so'ngra Intel Toshiba va Nokia kompaniyalarini ham jalb qildi. 1998 yil may oyida Bluetooth SIG IBM va Ericsson bilan birgalikda ta'sischilar va jami beshta a'zo sifatida ishga tushirildi: Ericsson, Intel, Nokia, Toshiba va IBM.
Birinchi iste'molchi Bluetooth qurilmasi 1999 yilda ishlab chiqarilgan. COMDEX-da "Best of show Technology Technology" mukofotiga sazovor bo'lgan qo'llarsiz mobil eshitish vositasi. Birinchi Bluetooth mobil telefoni Ericsson T36 edi, lekin u qayta ko'rib chiqilgan edi T39 2001 yilda javonlarni saqlashga muvaffaq bo'lgan model. Shu bilan birga, IBM 2001 yil oktyabr oyida IBM ThinkPad A30 ni taqdim etdi, bu esa o'rnatilgan Bluetooth bilan birinchi noutbuk edi.
Bluetooth-ning maishiy elektronika mahsulotlariga erta tatbiq etilishi Kostaning Mesa shahridagi (Kaliforniya shtati, AQSh) Vosi Technologies-da bo'lib o'tdi, dastlab ta'sischilar Bejan Amini va Tom Devidson tomonidan nazorat qilingan. Vosi Technologies kompaniyasi ko'chmas mulk ishlab chiqaruvchisi Ivano Stegmenga tomonidan 6085078 raqamli Amerika Qo'shma Shtatlarining Patenti bilan uyali telefon va transport vositasining audio tizimi o'rtasidagi aloqa uchun yaratilgan. O'sha paytda Sony / Ericsson AQShda Nokia va Motorola tomonidan ustun bo'lgan uyali telefon bozorida ozgina ulushga ega edi. 1990-yillarning oxiridan boshlab Motorola bilan mo'ljallangan litsenziyalash shartnomasi bo'yicha olib borilayotgan muzokaralar tufayli Vosi birinchi bo'lib ishlab chiqilgan boshqa qurilmalarning niyati, integratsiyasi va dastlabki ishlab chiqarilishi to'g'risida oshkor eta olmadi.Aqlli uy "Internetga ulangan qurilmalar.
Vosi tizimga transport vositasidan tarmoqdagi boshqa qurilmalarga simli ulanmasdan aloqa qilish uchun vosita kerak edi, shuning uchun Bluetooth tanlangan aloqa usuli edi, chunki WiFi hali ham osonlikcha mavjud emas yoki ommaviy bozorda qo'llab-quvvatlanmagan. Vosi Vosi Cello integratsiyalashgan avtoulov tizimini va boshqa ba'zi bir internetga ulangan qurilmalarni ishlab chiqara boshlagan, ulardan biri Bluetooth-ga ulangan Vosi Symphony nomli stol usti qurilmasi bo'lishi kerak edi. Motorola bilan muzokaralar olib borishda Vosi Bluetooth-ni o'z qurilmalariga qo'shish niyatini taqdim etdi va oshkor qildi. 2000-yillarning boshlarida a huquqiy kurash Vosi va Motorola o'rtasida paydo bo'ldi, bu esa qurilmalarning chiqarilishini muddatsiz to'xtatib qo'ydi. Keyinchalik, Motorola uni o'z qurilmalarida amalga oshirdi, bu esa o'sha paytdagi katta bozor ulushi tufayli ommaviy bozorda Bluetooth-ning sezilarli darajada tarqalishini boshladi.
Amalga oshirish
Bluetooth 2.402 va 2.480 oralig'ida ishlaydi Gigagertsli yoki 2.400 va 2.4835 GHz, shu jumladan qo'riqlash guruhlari 2 Pastki uchida MGts kengligi va 3,5 Yuqori qismida MGts kengligi.[18] Bu global litsenziyasiz (lekin tartibga solinmagan) sanoat, ilmiy va tibbiyotda (ISM ) 2.4 Gigagertsli qisqa diapazonli radiochastota diapazoni. Bluetooth deb nomlangan radio texnologiyasidan foydalanadi chastotali sakrashli spektr. Bluetooth uzatilgan ma'lumotlarni paketlarga ajratadi va har bir paketni 79 ta belgilangan Bluetooth kanallaridan biriga uzatadi. Har bir kanalning o'tkazuvchanligi 1 ga teng MGts. Odatda 1600 ni bajaradi sekundiga sakrash, bilan moslashuvchan chastota-sakrash (AFH) yoqilgan.[18] Bluetooth kam energiya 2. foydalanadi 40 kanalni o'z ichiga olgan MGts oralig'i.[19]
Dastlab, Gauss chastotasini almashtirish klavishi (GFSK) modulyatsiyasi mavjud bo'lgan yagona modulyatsiya sxemasi edi. Bluetooth 2.0 + EDR joriy qilinganidan beri, π / 4-DQPSK (differentsial kvadratura fazasini almashtirish klavishi) va 8-DPSK modulyatsiyasi ham mos keluvchi qurilmalar orasida ishlatilishi mumkin. GFSK bilan ishlaydigan qurilmalar asosiy tezlik (BR) rejimida ishlaydi, bu erda bir zumda bit tezligi 1 dan Mbit / s mumkin. Enhanced Data Rate (EDR) atamasi π / 4-DPSK va 8-DPSK sxemalarini tavsiflash uchun ishlatiladi, ularning har biri 2 va 3 ni beradi Mbit / s. Ushbu (BR va EDR) rejimlarning Bluetooth radiotexnologiyasidagi kombinatsiyasi a deb tasniflanadi BR / EDR radiosi.
2019 yilda Apple kengaytmani nashr etdi [1] 8Mbit / s gacha tezlikni qo'llab-quvvatlaydigan HDR deb nomlangan.
Bluetooth - bu paketga asoslangan protokol bilan master / qul me'morchiligi. Bitta xo'jayin a-da ettita qul bilan gaplashishi mumkin pikonet. Berilgan pikonetdagi barcha qurilmalar usta tomonidan taqdim etilgan soatni paketlar almashinuvi uchun asos sifatida ishlatadilar. Asosiy soat 312,5 davr bilan belgilanadi ms, so'ngra ikkita soat belgisi 625 uyani tashkil qiladi va ikkita uyasi 1250 juftlik juftligini tashkil qiladi .s. Oddiy bitta uyali paketlarda master juft uyalarda uzatadi va toq uyalarda qabul qiladi. Qul, aksincha, juft uyalarda qabul qiladi va g'alati uyalarda uzatadi. Paketlar uzunligi 1,3 yoki 5 bo'lishi mumkin, ammo barcha holatlarda xo'jayinning uzatilishi juft uyalardan, qul esa g'alati uyalardan boshlanadi.
Yuqorida keltirilgan 4.0-spetsifikatsiyada kiritilgan Bluetooth-ning past energiyasi bundan mustasno bir xil spektrdan foydalanadi, ammo boshqacha.
Aloqa va aloqa
Magistr BR / EDR Bluetooth qurilmasi pikonetda (Bluetooth texnologiyasidan foydalanadigan maxsus kompyuter tarmog'i) maksimal etti qurilmalar bilan aloqa o'rnatishi mumkin, ammo barcha qurilmalar bu darajaga erisha olmaydi. Qurilmalar kelishuvga binoan rollarni almashtirishi mumkin va qul masterga aylanishi mumkin (masalan, telefonga ulanishni boshlovchi naushnik albatta usta sifatida boshlanadi - ulanish tashabbuskori sifatida boshlanadi, lekin keyinchalik qul sifatida ishlashi mumkin).
Bluetooth yadrosi spetsifikatsiyasi a hosil qilish uchun ikki yoki undan ortiq pikonetlarning ulanishini ta'minlaydi Internet, unda ma'lum qurilmalar bir vaqtning o'zida bitta pikonetda asosiy rolni, ikkinchisida esa qul rolini o'ynaydi.
Istalgan vaqtda ma'lumotlar asosiy va boshqa qurilmalar o'rtasida uzatilishi mumkin (kam ishlatiladigan eshittirish rejimidan tashqari). Magistr qaysi qul qurilmasiga murojaat qilishni tanlaydi; odatda, u bir qurilmadan ikkinchisiga tez o'zgaradi dumaloq robin moda. Qaysi qulga murojaat qilishni xo'jayin o'zi tanlaganligi sababli, qul (nazariy jihatdan) har bir qabul qilish uyasida tinglashi kerak, xo'jayin bo'lish qul bo'lishdan ko'ra engilroq yuk. Etti qulning xo'jayini bo'lish mumkin; bir nechta xo'jayinning quli bo'lish mumkin. Spetsifikatsiyalar spektrlarda talab qilinadigan xatti-harakatlarga nisbatan noaniq.[20]
Foydalanadi
| Sinf | Maks. ruxsat etilgan quvvat | Turi. oralig'i[2] (m) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (mVt) | (dBm ) | ||
| 1 | 100 | 20 | ~100 |
| 1.5 (BT 5 jild 6 qism A qism 3-bo'lim) | 10 | 10 | ~20 |
| 2 | 2.5 | 4 | ~10 |
| 3 | 1 | 0 | ~1 |
| 4 | 0.5 | −3 | ~0.5 |
Bluetooth - bu simni almashtirishning standart protokoli bo'lib, u asosan kam quvvat sarf qilish uchun mo'ljallangan bo'lib, arzon narxlarga asoslangan qisqa diapazonga ega qabul qilgich mikrochiplar har bir qurilmada.[21] Qurilmalar radio (eshittirish) aloqa tizimidan foydalanganligi sababli, ular bir-birlarining vizual ko'rinishida bo'lishlari shart emas; ammo, a kvazi optik simsiz yo'l hayotga mos bo'lishi kerak.[22] Range kuch darajasiga bog'liq, ammo samarali diapazonlar amalda farq qiladi. "Sinflar bo'yicha Bluetooth qurilmalari oralig'i" jadvaliga qarang.
Rasmiy ravishda 3-sinf radiolari 1 metrgacha (3 fut), ko'pincha mobil qurilmalarda joylashgan 2-sinfga, 10 metrga (33 fut) va 1-sinfga, asosan sanoat uchun mo'ljallangan holatlarda, 100 metrga (300 fut) ega. .[2] Bluetooth Marketing shuni anglatadiki, 1-sinf oralig'i ko'p hollarda 20-30 metr (66-98 fut), 2-sinf esa 5-10 metr (16-33 fut).[1] Berilgan havola orqali erishilgan haqiqiy diapazon havolaning ikkala uchidagi asboblarning sifatiga, shuningdek, ular orasidagi havo sharoitlariga va boshqa omillarga bog'liq bo'ladi.
Samarali diapazon tarqalish shartlari, materialning qamrovi, ishlab chiqarish namunalarining o'zgarishi, antenna konfiguratsiyasi va batareyaning holatiga qarab farq qiladi. Ko'pgina Bluetooth ilovalari ichki sharoitga mo'ljallangan, bu erda devorlarning susayishi va signal aks etishi sababli signallarning pasayishi Bluetooth mahsulotlarining belgilangan ko'rish oralig'idan ancha past bo'ladi.
Aksariyat Bluetooth ilovalari batareyadan quvvat oladigan 2-sinf qurilmalari bo'lib, havolaning boshqa uchi 1-sinf yoki 2-sinf moslamasi bo'ladimi-yo'qmi, unchalik katta emas, chunki pastroq quvvatga ega qurilma intervalgacha cheklovni o'rnatishga intiladi. Ba'zi hollarda, ma'lumotlar zanjirining samarali doirasi 2-sinf qurilmasi odatdagi 2-sinf qurilmasiga qaraganda yuqori sezgirlik va uzatish quvvatiga ega bo'lgan 1-sinf qabul qiluvchi-uzatgichga ulanganda kengaytirilishi mumkin.[23] Biroq, asosan, 1-sinf qurilmalari 2-sinf qurilmalariga o'xshash sezgirlikka ega. Ikkala 1-darajali qurilmalarni yuqori sezgirlik va yuqori quvvat bilan ulash, dastur talab qiladigan o'tkazuvchanlikka qarab, odatdagi 100 metrdan ancha yuqori bo'lishi mumkin. Ba'zi bunday qurilmalar qonuniy chiqindilar miqdoridan oshmasdan, xuddi shunday ikkita moslama o'rtasida 1 km gacha va undan uzoq masofada ochiq maydonlarni o'tkazishga imkon beradi.[24][25][26]
Bluetooth yadrosi spetsifikatsiyasi 10 metrdan (33 fut) kam bo'lmagan masofani taqiqlaydi, ammo haqiqiy diapazonda yuqori chegara yo'q. Har bir holat uchun zarur bo'lgan oraliqni ta'minlash uchun ishlab chiqaruvchilarning dasturlarini sozlash mumkin.[2]
Bluetooth profili
Bluetooth simsiz texnologiyasidan foydalanish uchun qurilma mumkin bo'lgan ilovalarning ta'rifi bo'lgan va boshqa Bluetooth qurilmalari bilan aloqa qilish uchun Bluetooth-ni ishlatadigan qurilmalarning umumiy xatti-harakatlarini aniqlaydigan ba'zi bir Bluetooth rejimlarini izohlashi kerak. Ushbu profillar parametrlashni sozlash va aloqani boshidan boshqarish uchun sozlamalarni o'z ichiga oladi. Profillarga rioya qilish ikki yo'nalishli aloqa samarali bo'lgunga qadar parametrlarni uzatish uchun vaqtni tejaydi. Turli xil dastur turlarini tavsiflovchi yoki qurilmalar uchun holatlardan foydalanadigan Bluetooth profillarining keng doirasi mavjud.[27][28]
Arizalar ro'yxati

- Simsiz boshqarish va mobil telefon bilan aloqa handsfree naushnik. Bu mashhurlikka erishgan dastlabki dasturlardan biri edi.[29]
- Uyali telefon va Bluetooth-ga mos keladigan avtomobil stereo tizimining simsiz boshqaruvi va aloqasi (va ba'zan) SIM-karta va avtomobil telefoni o'rtasida[30][31]).
- Smartfon va a o'rtasidagi simsiz aloqa aqlli qulf eshiklarni ochish uchun.
- IOS va Android qurilmalaridagi telefonlar, planshetlar va ko'chma qurilmalarni simsiz boshqarish va ular bilan aloqani o'rnatish simsiz karnaylar.[32]
- Simsiz Bluetooth eshitish vositasi va Interkom. Idiomatik ma'noda garniturani ba'zan "Bluetooth" deb ham atashadi.
- Ovozni simsiz uzatish minigarnituralar aloqa qobiliyatiga ega yoki bo'lmagan holda.
- Bluetooth bilan ishlaydigan fitness qurilmalari tomonidan to'plangan ma'lumotlarning telefonga yoki kompyuterga simsiz uzatilishi.[33]
- Cheklangan joyda va kam tarmoqli kengligi zarur bo'lgan shaxsiy kompyuterlar o'rtasida simsiz tarmoq.[34]
- Kompyuterning kirish va chiqish moslamalari bilan simsiz aloqa, eng keng tarqalgan sichqoncha, klaviatura va printer.
- Qurilmalar o'rtasida fayllarni, aloqa ma'lumotlarini, taqvim uchrashuvlarini va eslatmalarni uzatish OBEX[a] va kataloglarni almashish FTP orqali.[35]
- Oldingi simlarni almashtirish RS-232 sinov uskunasidagi ketma-ket aloqa, GPS qabul qiluvchilar, tibbiy asbob-uskunalar, shtrix-skanerlar va transport vositalarini boshqarish vositalari.
- Boshqarish uchun qaerda infraqizil ko'pincha ishlatilgan.
- Kamroq tarmoqli kengligi bo'lgan ilovalar uchun USB tarmoqli kengligi talab qilinmaydi va simsiz ulanish zarur.
- Bluetooth-ni qo'llab-quvvatlaydigan reklama yig'ish vositalaridan kichik, boshqa reklamalarni Bluetooth qurilmalariga yuborish.[36]
- Ikkala sanoat chekilgani o'rtasida simsiz ko'prik (masalan, PROFINET ) tarmoqlar.
- Ettinchi va sakkizinchi avlod o'yin konsollari kabi Nintendo "s Wii,[37] va Sony "s PlayStation 3 tegishli simsiz tekshirgichlar uchun Bluetooth-dan foydalaning.
- Simsiz modem sifatida ma'lumotlarga ega bo'lgan mobil telefondan foydalangan holda shaxsiy kompyuterlarda yoki PDA-larda Internetga ulanish.
- Tibbiy asboblardan mobil telefonga sog'liqni saqlash sensori ma'lumotlarini qisqa masofaga uzatish, stol usti qutisi yoki bag'ishlangan tele salomatlik qurilmalar.[38][39]
- Ruxsat berish a DECT yaqin atrofdagi mobil telefon nomidan qo'ng'iroq qilish va javob berish uchun telefon.
- Haqiqiy vaqtda joylashishni aniqlash tizimlari (RTLS) "kuzatilgan ob'ektlarga biriktirilgan yoki ichiga o'rnatilgan" tugunlar "yoki" teglar "va ushbu teglardan simsiz signallarni qabul qiladigan va ishlov beradigan" o'quvchilar "yordamida real vaqtda ob'ektlarning joylashishini kuzatish va aniqlash uchun ishlatiladi. ularning joylashgan joylarini aniqlang.[40]
- Ob'ektlarning o'g'irlanishi yoki yo'qolishining oldini olish uchun mobil telefonlarda shaxsiy xavfsizlik dasturi. Himoyalangan narsada telefon bilan doimiy aloqada bo'lgan Bluetooth markeri (masalan, yorliq) mavjud. Agar aloqa uzilib qolsa (marker telefon doirasidan tashqarida bo'lsa), signal beriladi. Bu shuningdek a sifatida ishlatilishi mumkin bortdan odam signal. Ushbu texnologiyadan foydalangan mahsulot 2009 yildan beri mavjud.[41]
- Kalgari, Alberta, Kanadadagi yo'llar harakati bo'limi sayohatchilarning Bluetooth qurilmalaridan to'plangan ma'lumotlardan foydalanib, avtoulovchilarning sayohat vaqtlari va tirbandligini taxmin qiladi.[42]
- Ovozni simsiz uzatish (ishonchli alternativa FM transmitterlari )
- Nyukasl universiteti 2017 da Nabeel Fattah tomonidan vizual kortikal implant qurilmasiga jonli video oqim.[43]
- Ulanish harakatni boshqarish moslamalari VR minigarniturasidan foydalanganda kompyuterga
Wi-Fi-ga qarshi Bluetooth (IEEE 802.11)
Bluetooth va Wi-fi (Wi-Fi - bu foydalanadigan mahsulotlar uchun tovar nomi IEEE 802.11 standartlar) o'xshash dasturlarga ega: tarmoqlarni sozlash, fayllarni bosib chiqarish yoki uzatish. Wi-Fi ulanish uchun yuqori tezlikdagi kabelni almashtirish uchun mo'ljallangan mahalliy tarmoq ish joylarida yoki uyda kirish. Ushbu toifadagi dasturlar ba'zan chaqiriladi simsiz lokal tarmoqlar (WLAN). Bluetooth portativ uskunalar va uning ilovalari uchun mo'ljallangan edi. Ilovalar toifasi simsiz sifatida ko'rsatilgan shaxsiy tarmoq tarmog'i (WPAN). Bluetooth har qanday sharoitda shaxsiy olib boriladigan turli xil ilovalardagi kabellarni almashtirish va shuningdek, uydagi aqlli energiya funksiyalari (termostatlar va boshqalar) kabi aniq joylashuv dasturlari uchun ishlaydi.
Wi-Fi va Bluetooth ularning qo'llanilishi va ishlatilishida ma'lum darajada bir-birini to'ldiradi. Wi-Fi odatda kirish nuqtasi markazida joylashgan bo'lib, kirish nuqtasi orqali yo'naltirilgan barcha trafik bilan assimetrik mijoz-server aloqasi, Bluetooth esa odatda nosimmetrik bo'lib, ikkita Bluetooth qurilmasi o'rtasida joylashgan. Ikkala qurilma minigarnituralar va masofadan boshqarish pultlaridagi kabi tugmachani bosish kabi minimal konfiguratsiya bilan ulanishi kerak bo'lgan oddiy dasturlarda Bluetooth yaxshi ishlaydi, Wi-Fi esa ba'zi darajadagi mijozlar konfiguratsiyasi mumkin bo'lgan va yuqori tezlikni talab qiladigan dasturlarda yaxshiroq ishlaydi, ayniqsa, kirish tuguni orqali tarmoqqa kirish uchun. Biroq, Bluetooth-ga kirish nuqtalari mavjud va Wi-Fi-da vaqtincha ulanish mumkin, ammo bu shunchaki Bluetooth kabi emas. Wi-Fi Direct yaqinda Wi-Fi-ga ko'proq Bluetooth-ga o'xshash vaqtinchalik funksiyani qo'shish uchun ishlab chiqilgan.[44]
Qurilmalar

Bluetooth telefonlar kabi ko'plab mahsulotlarda mavjud. ma'ruzachilar, planshetlar, media pleerlar, robototexnika tizimlari, noutbuklar va konsol o'yin uskunalari hamda yuqori aniqlikda minigarnituralar, modemlar, eshitish vositalari[45] va hatto soatlar.[46] Bluetooth-dan foydalanadigan turli xil qurilmalar va naushniklarning zamonaviy eskirishi bilan bir qatorda jaklar Apple, Google va boshqa kompaniyalar tomonidan va FCC tomonidan tartibga solinmaganligi sababli, texnologiya aralashishga moyil.[47] Shunga qaramay, Bluetooth past o'tkazuvchanlik holatida bir-biriga yaqin bo'lgan ikki yoki undan ortiq qurilmalar o'rtasida ma'lumot uzatishda foydalidir. Bluetooth odatda ovozli ma'lumotlarni telefonlar bilan (ya'ni, Bluetooth eshitish vositasi bilan) yoki qo'lda ishlaydigan kompyuterlar (fayllarni uzatish) bilan bayt ma'lumotlarini uzatish uchun ishlatiladi.
Bluetooth protokollari qurilmalar o'rtasida xizmatlarni topishni va sozlashni soddalashtiradi.[48] Bluetooth qurilmalari ular ko'rsatadigan barcha xizmatlarni reklama qilishlari mumkin.[49] Bu xizmatlardan foydalanishni osonlashtiradi, chunki ko'proq xavfsizlik, tarmoq manzili va ruxsat konfiguratsiyasi boshqa ko'plab tarmoq turlariga qaraganda avtomatlashtirilishi mumkin.[48]
Kompyuterga talablar


O'rnatilgan Bluetooth-ga ega bo'lmagan shaxsiy kompyuter, kompyuterni Bluetooth qurilmalari bilan aloqa o'rnatishga imkon beradigan Bluetooth adapteridan foydalanishi mumkin. Ba'zilar esa ish stoli kompyuterlar va eng so'nggi noutbuklar o'rnatilgan Bluetooth radiosi bilan ta'minlangan, boshqalari tashqi adapterni talab qiladi, odatda kichik USB shaklida "dongle."
Oldingisidan farqli o'laroq, IrDA, har bir qurilma uchun alohida adapter kerak bo'lsa, Bluetooth bir nechta qurilmalarga bitta adapter orqali kompyuter bilan aloqa o'rnatishga imkon beradi.[50]
Operatsion tizimni amalga oshirish
Uchun Microsoft platformalar, Windows XP Service Pack 2 va SP3 versiyalari mahalliy ravishda Bluetooth v1.1, v2.0 va v2.0 + EDR bilan ishlaydi.[51] Oldingi versiyalarda foydalanuvchilar Bluetooth-adapterining o'zlarining haydovchilarini o'rnatishi kerak edi, ular Microsoft tomonidan bevosita qo'llab-quvvatlanmaydi.[52] Microsoft-ning o'z Bluetooth-donglari (Bluetooth-ning kompyuter qurilmalari bilan paketlangan) tashqi drayverlarga ega emas va shuning uchun kamida Windows XP Service Pack 2-ni talab qiladi. Windows Vista RTM / SP1 simsiz yoki Windows Vista SP2 uchun xususiyatlar to'plami Bluetooth v2.1 + EDR bilan ishlaydi. .[51] Windows 7 Bluetooth v2.1 + EDR va kengaytirilgan so'rovlarga javob (EIR) bilan ishlaydi.[51]Windows XP va Windows Vista / Windows 7 Bluetooth to'plamlari quyidagi Bluetooth profillarini tabiiy ravishda qo'llab-quvvatlaydi: PAN, SPP, DUN, HID, HCRP. Windows XP stekini boshqa profillar yoki yangi Bluetooth versiyalarini qo'llab-quvvatlaydigan uchinchi tomon stek bilan almashtirish mumkin. Windows Vista / Windows 7 Bluetooth to'plami, Microsoft stack-ni almashtirishni talab qilmasdan, sotuvchi tomonidan ta'minlangan qo'shimcha profillarni qo'llab-quvvatlaydi.[51] Odatda Bluetooth qurilmasidan to'liq foydalanish imkoniyatiga ega bo'lish uchun eng so'nggi sotuvchi drayverini va unga tegishli stekni o'rnatish tavsiya etiladi.
olma O'shandan beri mahsulotlar Bluetooth bilan ishlaydi Mac OS X v10.2, 2002 yilda chiqarilgan.[53]
Linux ikkita mashhur Bluetooth to'plamlari, BlueZ va Ftor. BlueZ to'plami aksariyat Linux yadrolariga kiritilgan va dastlab uni ishlab chiqqan Qualcomm.[54] Ilgari Bluedroid nomi bilan tanilgan ftor Android operatsion tizimiga kiritilgan va dastlab tomonidan ishlab chiqilgan Broadcom.[55]Tomonidan ishlab chiqilgan Affix stack ham mavjud Nokia. U bir vaqtlar ommabop bo'lgan, ammo 2005 yildan beri yangilanmagan.[56]
FreeBSD v5.0 versiyasidan beri Bluetooth-ni o'z ichiga oladi netgraf.[57]
NetBSD v4.0 versiyasidan beri Bluetooth-ni o'z ichiga oladi.[58] Uning Bluetooth to'plami portga o'tkazildi OpenBSD ammo, keyinchalik OpenBSD uni buzilmagan deb olib tashladi.[59][60]
DragonFly BSD 1.11 (2008) dan beri NetBSD-ning Bluetooth-ni amalga oshirmoqda.[61] A netgraf -dan asoslangan amalga oshirish FreeBSD daraxtda ham mavjud edi, ehtimol 2014-11-15 yilgacha o'chirib qo'yilgan va ko'proq ishni talab qilishi mumkin.[62][63]
Texnik xususiyatlari va xususiyatlari
Texnik xususiyatlar tomonidan rasmiylashtirildi Bluetooth maxsus foizlar guruhi (SIG) va 1998 yil 20 mayda rasmiy ravishda e'lon qilingan.[64] Bugungi kunda uning dunyodagi 30 mingdan ziyod kompaniyalari a'zosi.[65] Tomonidan tashkil etilgan Ericsson, IBM, Intel, Nokia va Toshiba va keyinchalik ko'plab boshqa kompaniyalar qo'shildi.
Bluetooth standartlarining barcha versiyalari qo'llab-quvvatlanadi pastga qarab muvofiqligi.[66] Bu so'nggi barcha eski versiyalarni qamrab olishga imkon beradi.
Bluetooth Core Specification Working Group (CSWG) asosan 4 turdagi texnik xususiyatlarni ishlab chiqaradi:
- Bluetooth yadrosi spetsifikatsiyasi, chiqarish davri odatda bir necha yilni tashkil qiladi
- Yadro spetsifikatsiyasi qo'shimchasi (CSA), chiqarish davri yiliga bir necha marta qattiq bo'lishi mumkin
- Asosiy spetsifikatsiya qo'shimchalari (CSS) juda tez chiqarilishi mumkin
- Errata (foydalanuvchi qayd yozuvida mavjud: Xatolik bilan kirish )
Bluetooth 1.0 va 1.0B
1.0 va 1.0B versiyalari[iqtibos kerak ] ko'plab muammolarga duch keldi va ishlab chiqaruvchilar o'z mahsulotlarini bir-biriga mos keltirishda qiynaldilar. 1.0 va 1.0B versiyalarida, shuningdek, Bluetooth muhitida foydalanish rejalashtirilgan ba'zi xizmatlar uchun katta to'siq bo'lgan ulanish jarayonida majburiy ravishda Bluetooth qurilmasi manzilini (BD_ADDR) uzatishni o'z ichiga olgan (protokol darajasida noma'lumlikni keltirib chiqaradi).
Bluetooth 1.1
- Sifatida tasdiqlangan IEEE standarti 802.15.1-2002[67]
- V1.0B texnik xususiyatlarida topilgan ko'plab xatolar tuzatildi.
- Shifrlanmagan kanallarni qo'shish imkoniyati qo'shildi.
- Signal kuchining ko'rsatkichi (RSSI ).
Bluetooth 1.2
Asosiy yaxshilanishlarga quyidagilar kiradi:
- Tezroq ulanish va kashfiyot
- Moslashuvchan chastotali sakrashli spektr (AFH), bu qarshilikni yaxshilaydi radio chastotali shovqin sakrash ketma-ketligida gavjum chastotalardan foydalanishni oldini olish orqali.
- Amaliyotda v1.1 ga qaraganda yuqori uzatish tezligi 721 kbit / s gacha.[68]
- Buzilgan paketlarni qayta uzatishga imkon berish orqali audio havolalarning ovozli sifatini yaxshilaydigan va ixtiyoriy ravishda ma'lumotlarning bir vaqtning o'zida yaxshi uzatilishini ta'minlash uchun ovozning kechikishini oshiradigan kengaytirilgan sinxron aloqalar (eSCO).
- Xost tekshiruvi interfeysi (HCI) uch simli operatsiya UART.
- Sifatida tasdiqlangan IEEE standarti 802.15.1-2005[69]
- L2CAP uchun oqimni boshqarish va qayta uzatish rejimlari taqdim etildi.
Bluetooth 2.0 + EDR
Bluetooth yadrosi spetsifikatsiyasining ushbu versiyasi 2005 yilgacha chiqarilgan edi. Asosiy farq shundaki, tezroq ma'lumotlarning kengaytirilgan tezligi (EDR) ma'lumotlar uzatish. EDR bit tezligi 3 ga teng Mbit / s, garchi ma'lumotlarni uzatishning maksimal tezligi (paketlararo vaqt va tasdiqlash uchun imkon beradi) 2.1 ga teng Mbit / s.[68] EDR ning kombinatsiyasidan foydalaniladi GFSK va fazani almashtirish klavishi modulyatsiya (PSK) ikkita variant bilan, π / 4-DQPSK va 8-DPSK.[70] EDR kamaytirilgan quvvat sarfini kamaytirishi mumkin ish aylanishi.
Spetsifikatsiya sifatida nashr etilgan Bluetooth v2.0 + EDR, bu shuni anglatadiki, EDR ixtiyoriy xususiyatdir. EDR-dan tashqari, v2.0 spetsifikatsiyasi boshqa kichik yaxshilanishlarni ham o'z ichiga oladi va mahsulotlar yuqori ma'lumotlar tezligini qo'llab-quvvatlamasdan "Bluetooth v2.0" ga muvofiqligini talab qilishi mumkin. Hech bo'lmaganda bitta tijorat qurilmasi ma'lumot varag'ida "EDR holda Bluetooth v2.0" deb yozadi.[71]
Bluetooth 2.1 + EDR
Bluetooth Core Specification Version 2.1 + EDR Bluetooth SIG tomonidan 2007 yil 26 iyulda qabul qilingan.[70]
V2.1-ning sarlavha xususiyati xavfsiz oddiy juftlik (SSP): bu Bluetooth qurilmalari uchun ulanish tajribasini yaxshilaydi, shu bilan birga xavfsizlik va foydalanish kuchini oshiradi.[72]
2.1 versiyasi, shu jumladan, boshqa har xil yaxshilanishlarga imkon beradi kengaytirilgan so'rovga javob (EIR), bu ulanishdan oldin qurilmalarni yaxshiroq filtrlash imkoniyatini berish uchun so'rov jarayonida qo'shimcha ma'lumot beradi; va past hidlash, past quvvat rejimida quvvat sarfini kamaytiradi.
Bluetooth 3.0 + HS
Bluetooth Core Specification ning 3.0 versiyasi + HS[70] Bluetooth SIG tomonidan 2009 yil 21 aprelda qabul qilingan. Bluetooth v3.0 + HS ma'lumotlar uzatishning nazariy tezligini 24 Mbit / s gacha beradi, lekin Bluetooth aloqasi orqali emas. Buning o'rniga, Bluetooth aloqasi muzokaralar olib borish va o'rnatish uchun ishlatiladi va ma'lumotlarning yuqori tezligi trafikni ajratilgan holda amalga oshiriladi 802.11 havola
Asosiy yangi xususiyat - bu AMP (Alternative MAC / PHY) 802.11 yuqori tezlikda transport sifatida. Spetsifikatsiyaning yuqori tezlikli qismi majburiy emas va shuning uchun faqat "+ HS" logotipi aks etadigan qurilmalar aslida Bluetooth-ni 802.11 yuqori tezlikda ma'lumotlarni uzatishni qo'llab-quvvatlaydi. "+ HS" qo'shimchasiz Bluetooth v3.0 qurilmasi faqat Core Specification Version 3.0-da taqdim etilgan xususiyatlarni qo'llab-quvvatlash uchun talab qilinadi.[73] yoki undan oldingi asosiy spetsifikatsiya qo'shimchasi 1.[74]
- L2CAP Kengaytirilgan rejimlar
- Kengaytirilgan Retransmission Mode (ERTM) ishonchli L2CAP kanalini amalga oshiradi, Streaming Mode (SM) esa qayta uzatish yoki oqim nazorati bo'lmagan ishonchsiz kanalni amalga oshiradi. Asosiy spetsifikatsiya qo'shimchasi 1-da kiritilgan.
- Muqobil MAC / PHY
- Muqobil variantni ishlatishga imkon beradi MAC va PHY Bluetooth profil ma'lumotlarini tashish uchun. Bluetooth radiosi hali ham qurilmani topish, dastlabki ulanish va profilni sozlash uchun ishlatiladi. Biroq, katta miqdordagi ma'lumotlar yuborilishi kerak bo'lganida, yuqori tezlikda ishlaydigan alternativ MAC PHY 802.11 (odatda Wi-Fi bilan bog'liq) ma'lumotlarni uzatadi. Bu shuni anglatadiki, Bluetooth ishlamay qolganda tasdiqlangan past quvvatli ulanish modellaridan foydalanadi va katta miqdordagi ma'lumotlarni yuborishi kerak bo'lgan tezroq radio. AMP havolalari kengaytirilgan L2CAP rejimlarini talab qiladi.
- Bir tarmoqli ulanishsiz ma'lumotlar
- L2CAP aniq kanalini o'rnatmasdan xizmat ma'lumotlarini yuborishga ruxsat beradi. U foydalanuvchi harakati va ma'lumotlarni qayta ulash / uzatish o'rtasida kam kechikishni talab qiladigan ilovalar tomonidan foydalanishga mo'ljallangan. Bu faqat kichik hajmdagi ma'lumotlarga mos keladi.
- Kengaytirilgan quvvat nazorati
- Ochiq pastadirli quvvatni boshqarishni olib tashlash va shuningdek, EDR uchun qo'shilgan yangi modulyatsiya sxemalari tomonidan kiritilgan quvvatni boshqarishdagi noaniqliklarni aniqlash uchun quvvatni boshqarish xususiyatini yangilaydi. Kengaytirilgan quvvat nazorati kutilgan xatti-harakatni belgilab, noaniqliklarni yo'q qiladi. Xususiyat, shuningdek, yopiq pastadirli quvvatni boshqarishni qo'shadi, ya'ni RSSI filtrlash javob qabul qilinganda boshlanishi mumkin. Bundan tashqari, "to'g'ridan-to'g'ri maksimal quvvatga o'ting" so'rovi kiritildi. Bu, odatda, foydalanuvchi o'z telefonini naushnikning qarama-qarshi tomonidagi cho'ntagiga qo'yganda kuzatiladigan eshitish vositasining yo'qolishi muammosini hal qilishi kutilmoqda.
Ultra keng tarmoqli
Bluetooth v3.0-ning yuqori tezlikli (AMP) xususiyati dastlab mo'ljallangan edi UWB, lekin Bluetooth uchun mo'ljallangan UWB ta'mi uchun mas'ul bo'lgan WiMedia Alliance 2009 yil mart oyida tarqatib yuborilishini e'lon qildi va oxir-oqibat UWB Core v3.0 spetsifikatsiyasidan chiqarildi.[75]
2009 yil 16 martda WiMedia Alliance WiMedia uchun texnologiya uzatish bo'yicha shartnomalar tuzayotganini e'lon qildi Ultra keng tarmoqli (UWB) texnik xususiyatlari. WiMedia barcha mavjud va kelgusi texnik xususiyatlarni, shu jumladan kelajakda yuqori tezlik va quvvatni optimallashtirishni amalga oshirishni Bluetooth maxsus qiziqish guruhiga (SIG) o'tkazdi, Simsiz USB Promouterlar guruhi va USB amalga oshiruvchilar forumi. Texnologiyalarni uzatish, marketing va tegishli ma'muriy narsalar muvaffaqiyatli bajarilgandan so'ng, WiMedia Alliance o'z faoliyatini to'xtatdi.[76][77][78][79][80]
2009 yil oktyabr oyida Bluetooth maxsus foizlar guruhi muqobil MAC / PHY, Bluetooth v3.0 + HS echimining bir qismi sifatida UWB-ni ishlab chiqarishni to'xtatdi. Birinchisi kichik, ammo ahamiyatli WiMedia a'zolari uchun zarur bo'lgan shartnomalarni imzolamagan va imzolamagan IP o'tkazish. Bluetooth SIG endi uzoq muddatli yo'l xaritasi uchun boshqa variantlarni baholash jarayonida.[81][82][83]
Bluetooth 4.0
Bluetooth SIG Bluetooth Core Specification 4.0 versiyasini (Bluetooth Smart deb nomlangan) to'ldirdi va 2010 yil 30 iyundan qabul qilindi[yangilash]. Bunga kiradi Klassik Bluetooth, Bluetooth yuqori tezligi va Bluetooth kam energiya (BLE) protokollari. Bluetooth yuqori tezligi Wi-Fi-ga asoslangan va Classic Bluetooth eski Bluetooth protokollaridan iborat.
Bluetooth kam energiya ilgari Wibree nomi bilan tanilgan,[84] bu oddiy ulanishlarni tezkor ravishda shakllantirish uchun mutlaqo yangi protokollar to'plamiga ega bo'lgan Bluetooth v4.0 ning pastki qismidir. Bluetooth v1.0-dan v3.0-ga kiritilgan Bluetooth standart protokollariga muqobil ravishda, u juda past quvvatli dasturlarga va tanga xujayrasi. Chip dizaynlari ikki turdagi, ikkita rejimli, bitta rejimli va kengaytirilgan o'tgan versiyalarni amalga oshirishga imkon beradi.[85] Vaqtinchalik ismlar Wibree va Bluetooth ULP (Ultra Low Power) ishlatilmadi va BLE nomi bir muddat ishlatilgan. 2011 yil oxirida BLE-ning keng yuzi sifatida xostlar uchun "Bluetooth Smart Ready" va sensorlar uchun "Bluetooth Smart" yangi logotiplari taqdim etildi.[86]
Ga solishtirganda Klassik Bluetooth, Bluetooth Low Energy, quvvatni sarfini kamaytirish va sezilarli darajada kamaytirilgan quvvat sarfini ta'minlashga mo'ljallangan shunga o'xshash aloqa doirasi. Bluetooth qurilmalarining batareyaning ishlash muddatini uzaytirish bo'yicha BLE muhim rivojlanishni anglatadi.
- Bitta rejimli dasturda faqat past energiya protokoli to'plami amalga oshiriladi. Dialog yarim o'tkazgich,[87] STMikroelektronika,[88] AMICCOM,[89] KSS,[90] Shimoliy yarim o'tkazgich[91] va Texas Instruments[92] yagona rejimli Bluetooth Low Energy echimlarini chiqardi.
- Ikkala rejimni amalga oshirishda Bluetooth Smart funksiyasi mavjud Classic Bluetooth tekshirgichiga qo'shiladi. 2011 yil mart holatiga ko'ra[yangilash], quyidagi yarimo'tkazgichli kompaniyalar standartga javob beradigan chiplar mavjudligini e'lon qilishdi: Qualcomm-Atheros, KSS, Broadcom[93][94] va Texas Instruments. Mos keluvchi arxitektura Classic Bluetooth-ning barcha mavjud radiosi va funksiyalarini baham ko'radi, natijada Classic Bluetooth bilan taqqoslaganda narxlar sezilarli darajada oshmaydi.
Yuqori darajadagi integratsiyalashgan va ixcham qurilmalarni ishga tushiradigan narxni pasaytiradigan bir martalik chiplar ultra past quvvat rejimida ishlashni, oddiy qurilmani kashf etishni va quvvatni tejash va xavfsizlikni ta'minlash bilan ishonchli ma'lumotni bir nuqtadan ko'p nuqtaga uzatishni ta'minlaydigan engil bog'lovchi qatlamga ega. mumkin bo'lgan eng kam xarajat bilan shifrlangan ulanishlar.
4.0 versiyasidagi umumiy yaxshilanishlar orasida BLE rejimlarini osonlashtirish uchun zarur bo'lgan o'zgarishlar, shuningdek General Attribute Profile (GATT) va Security Manager (SM) xizmatlari mavjud. AES Shifrlash.
Asosiy spetsifikatsiya bo'yicha qo'shimcha 2 2011 yil dekabr oyida e'lon qilingan; u audio xost tekshiruvi interfeysi va yuqori tezlikda (802.11) protokolni moslashtirish qatlamini yaxshilaydi.
3-sonli asosiy spetsifikatsiya qo'shimchasi 2012 yil 24-iyulda qabul qilingan sanaga ega.
Asosiy spetsifikatsiya bo'yicha 4-qo'shimcha 2013 yil 12 fevralda qabul qilingan sanaga ega.
Bluetooth 4.1
Bluetooth SIG 2013 yil 4 dekabrda Bluetooth v4.1 spetsifikatsiyasini rasmiy ravishda qabul qilganligini e'lon qildi. Ushbu spetsifikatsiya apparat yangilanishi emas, balki Bluetooth Specification v4.0-ga dasturiy ta'minotning qo'shimcha yangilanishi hisoblanadi. Yangilanish Bluetooth Core Specification Addenda (CSA 1, 2, 3 & 4) ni o'z ichiga oladi va iste'molchilarga qulayligini yaxshilaydigan yangi xususiyatlarni qo'shadi. Bunga LTE-ni birgalikda qo'llab-quvvatlash, ommaviy ma'lumotlar almashinuvi kurslari va qurilmalarga bir vaqtning o'zida bir nechta rollarni qo'llab-quvvatlashga imkon berish orqali ishlab chiquvchilarning innovatsiyalariga yordam berish kiradi.[95]
Ushbu spetsifikatsiyaning yangi xususiyatlari quyidagilarni o'z ichiga oladi:
- Uyali aloqa simsiz xizmatining birgalikdagi mavjudligini bildiruvchi signalizatsiya
- Poezdlarni yalang'ochlash va umumiy interlaced skanerlash
- Kam bojxona davri yo'naltirilgan reklama
- L2CAP ulanishga yo'naltirilgan va ajratilgan kanallar, kreditga asoslangan oqim nazorati
- Ikki tomonlama rejim va topologiya
- LE bog'lanish qatlami topologiyasi
- 802.11n PAL
- Keng tarmoqli nutq uchun audio arxitekturani yangilash
- Ma'lumotlarni tezkor reklama qilish oralig'i
- Cheklangan kashfiyot vaqti[96]
E'tibor bering, ba'zi xususiyatlar v4.1 versiyasi chiqarilishidan oldin Core Specification Addend (CSA) da mavjud edi.
Bluetooth 4.2
2014 yil 2-dekabrda chiqarilgan, uchun xususiyatlarini taqdim etadi Internet narsalar.
Obodonlashtirishning asosiy yo'nalishlari:
- Kam energiya Xavfsiz ulanish bilan Ma'lumotlar to'plami Uzunlikni kengaytirish
- Havola qatlami Kengaytirilgan brauzer filtri siyosati bilan maxfiylik
- Internet protokoli Qo'llab-quvvatlash profili (IPSP) versiya 6 tayyor Bluetooth Smart narsalar ulangan uyni qo'llab-quvvatlash uchun
Eski Bluetooth apparati dasturiy ta'minotni yangilash orqali ma'lumotlar paketining uzunligini kengaytirish va maxfiylikni yaxshilash kabi 4.2 xususiyatlarga ega bo'lishi mumkin.[97][98]
Bluetooth 5
The Bluetooth SIG released Bluetooth 5 on 6 December 2016. Its new features are mainly focused on new Internet narsalar texnologiya. Sony was the first to announce Bluetooth 5.0 support with its Xperia XZ Premium in Feb 2017 during the Mobile World Congress 2017.[99] Samsung Galaxy S8 launched with Bluetooth 5 support in April 2017. In September 2017, the iPhone 8, 8 Plus va iPhone X launched with Bluetooth 5 support as well. olma also integrated Bluetooth 5 in its new HomePod offering released on 9 February 2018.[100] Marketing drops the point number; so that it is just "Bluetooth 5" (unlike Bluetooth 4.0).[iqtibos kerak ] The change is for the sake of "Simplifying our marketing, communicating user benefits more effectively and making it easier to signal significant technology updates to the market."[101]
Bluetooth 5 provides, for BLE, options that can double the speed (2 Mbit/s burst) at the expense of range, or up to fourfold the range at the expense of data rate. The increase in transmissions could be important for Internet narsalar devices, where many nodes connect throughout a whole house. Bluetooth 5 adds functionality for connectionless services such as location-relevant navigation[102] of low-energy Bluetooth connections.[103][104][105]
The major areas of improvement are:
- Slot Availability Mask (SAM)
- 2 Mbit/s PHY for LE
- LE Long Range
- High Duty Cycle Non-Connectable Advertising
- LE Advertising Extensions
- LE Channel Selection Algorithm #2
Features Added in CSA5 – Integrated in v5.0:
- Higher Output Power
The following features were removed in this version of the specification:
- Park shtati[106]
Bluetooth 5.1
The Bluetooth SIG presented Bluetooth 5.1 on 21 January 2019.
The major areas of improvement are:
- Angle of Arrival (AoA) and Angle of Departure (AoD) which are used for location and tracking of devices
- Advertising Channel Index
- GATT Caching
- Minor Enhancements batch 1:
- HCI support for debug keys in LE Secure Connections
- Sleep clock accuracy update mechanism
- ADI field in scan response data
- Interaction between QoS and Flow Specification
- Block Host channel classification for secondary advertising
- Allow the SID to appear in scan response reports
- Specify the behavior when rules are violated
- Periodic Advertising Sync Transfer
Features Added in Core Specification Addendum (CSA) 6 – Integrated in v5.1:
- Modellar
- Mesh-based model ierarxiya
The following features were removed in this version of the specification:
- Unit keys
Bluetooth 5.2
On 31 December 2019, the Bluetooth SIG published the Bluetooth Core Specification Version 5.2. The new specification adds new features:[107]
- LE Audio: Announced in January 2020 at CES tomonidan Bluetooth SIG, LE Audio will run on the Bluetooth kam energiya radio lowering battery consumption, and allow the protocol to carry sound and add features such as one set of headphones connecting to multiple audio sources or multiple headphones connecting to one source[108][109] It uses a new LC3 codec. BLE Audio will also add support for hearing aids.[110]
- Enhanced Attribute Protocol (EATT), an improved version of the Attribute Protocol (ATT)
- LE Power Control
- LE Isochronous Channels
Texnik ma'lumotlar
Arxitektura
Dasturiy ta'minot
Seeking to extend the compatibility of Bluetooth devices, the devices that adhere to the standard use an interface called HCI (Host Controller Interface) between the host device (e.g. laptop, phone) and the Bluetooth device (e.g. Bluetooth wireless headset).
High-level protocols such as the SDP (Protocol used to find other Bluetooth devices within the communication range, also responsible for detecting the function of devices in range), RFCOMM (Protocol used to emulate serial port connections) and TCS (Telephony control protocol) interact with the baseband controller through the L2CAP Protocol (Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol). The L2CAP protocol is responsible for the segmentation and reassembly of the packets.
Uskuna
The hardware that makes up the Bluetooth device is made up of, logically, two parts; which may or may not be physically separate. A radio device, responsible for modulating and transmitting the signal; and a digital controller. The digital controller is likely a CPU, one of whose functions is to run a Link Controller; and interfaces with the host device; but some functions may be delegated to hardware. The Link Controller is responsible for the processing of the baseband and the management of ARQ and physical layer FEC protocols. In addition, it handles the transfer functions (both asynchronous and synchronous), audio coding (e.g. SBC (codec) ) and data encryption. The CPU of the device is responsible for attending the instructions related to Bluetooth of the host device, in order to simplify its operation. To do this, the CPU runs software called Link Manager that has the function of communicating with other devices through the LMP protocol.
A Bluetooth device is a qisqa masofa simsiz qurilma. Bluetooth devices are uydirma kuni RF CMOS integral mikrosxema (RF davri ) chips.[5][111]
Bluetooth protocol stack
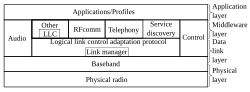
Bluetooth is defined as a layer protocol architecture consisting of core protocols, cable replacement protocols, telephony control protocols, and adopted protocols.[112] Mandatory protocols for all Bluetooth stacks are LMP, L2CAP and SDP. In addition, devices that communicate with Bluetooth almost universally can use these protocols: HCI and RFCOMM.[iqtibos kerak ]
Link Manager
The Link Manager (LM) is the system that manages establishing the connection between devices. It is responsible for the establishment, authentication and configuration of the link. The Link Manager locates other managers and communicates with them via the management protocol of the LMP link. To perform its function as a service provider, the LM uses the services included in the Link Controller (LC).The Link Manager Protocol basically consists of several PDUs (Protocol Data Units) that are sent from one device to another. The following is a list of supported services:
- Transmission and reception of data.
- Name request
- Request of the link addresses.
- Establishment of the connection.
- Authentication.
- Negotiation of link mode and connection establishment.
Xost tekshiruvi interfeysi
The Host Controller Interface provides a command interface for the controller and for the link manager, which allows access to the hardware status and control registers.This interface provides an access layer for all Bluetooth devices. The HCI layer of the machine exchanges commands and data with the HCI firmware present in the Bluetooth device. One of the most important HCI tasks that must be performed is the automatic discovery of other Bluetooth devices that are within the coverage radius.
Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol
The Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol (L2CAP) is used to multiplex multiple logical connections between two devices using different higher level protocols.Provides segmentation and reassembly of on-air packets.
Yilda Asosiy mode, L2CAP provides packets with a payload configurable up to 64 kB, with 672 bytes as the default MTU, and 48 bytes as the minimum mandatory supported MTU.
Yilda Retransmission and Flow Control modes, L2CAP can be configured either for isochronous data or reliable data per channel by performing retransmissions and CRC checks.
Bluetooth Core Specification Addendum 1 adds two additional L2CAP modes to the core specification. These modes effectively deprecate original Retransmission and Flow Control modes:
- Enhanced Retransmission Mode (ERTM)
- This mode is an improved version of the original retransmission mode. This mode provides a reliable L2CAP channel.
- Streaming Mode (SM)
- This is a very simple mode, with no retransmission or flow control. This mode provides an unreliable L2CAP channel.
Reliability in any of these modes is optionally and/or additionally guaranteed by the lower layer Bluetooth BDR/EDR air interface by configuring the number of retransmissions and flush timeout (time after which the radio flushes packets). In-order sequencing is guaranteed by the lower layer.
Only L2CAP channels configured in ERTM or SM may be operated over AMP logical links.
Service Discovery Protocol
The Service Discovery Protocol (SDP) allows a device to discover services offered by other devices, and their associated parameters. For example, when you use a mobile phone with a Bluetooth headset, the phone uses SDP to determine which Bluetooth profiles the headset can use (Headset Profile, Hands Free Profile (HFP), Kengaytirilgan audio tarqatish profili (A2DP) etc.) and the protocol multiplexer settings needed for the phone to connect to the headset using each of them. Each service is identified by a Umumjahon noyob identifikator (UUID), with official services (Bluetooth profiles) assigned a short form UUID (16 bits rather than the full 128).
Radio Frequency Communications
Radio Frequency Communications (RFCOMM) is a cable replacement protocol used for generating a virtual serial data stream. RFCOMM provides for binary data transport and emulates EIA-232 (formerly RS-232) control signals over the Bluetooth baseband layer, i.e., it is a serial port emulation.
RFCOMM provides a simple, reliable, data stream to the user, similar to TCP. It is used directly by many telephony related profiles as a carrier for AT commands, as well as being a transport layer for OBEX over Bluetooth.
Many Bluetooth applications use RFCOMM because of its widespread support and publicly available API on most operating systems. Additionally, applications that used a serial port to communicate can be quickly ported to use RFCOMM.
Bluetooth Network Encapsulation Protocol
The Bluetooth Network Encapsulation Protocol (BNEP) is used for transferring another protocol stack's data via an L2CAP channel.Its main purpose is the transmission of IP packets in the Personal Area Networking Profile.BNEP performs a similar function to SNAP in Wireless LAN.
Audio/Video Control Transport Protocol
The Audio/Video Control Transport Protocol (AVCTP) is used by the remote control profile to transfer AV/C commands over an L2CAP channel. The music control buttons on a stereo headset use this protocol to control the music player.
Audio/Video Distribution Transport Protocol
The Audio/Video Distribution Transport Protocol (AVDTP) is used by the advanced audio distribution (A2DP ) profile to stream music to stereo headsets over an L2CAP channel intended for video distribution profile in the Bluetooth transmission.
Telephony Control Protocol
The Telephony Control Protocol – Binary (TCS BIN) is the bit-oriented protocol that defines the call control signaling for the establishment of voice and data calls between Bluetooth devices. Additionally, "TCS BIN defines mobility management procedures for handling groups of Bluetooth TCS devices."
TCS-BIN is only used by the cordless telephony profile, which failed to attract implementers. As such it is only of historical interest.
Adopted protocols
Adopted protocols are defined by other standards-making organizations and incorporated into Bluetooth's protocol stack, allowing Bluetooth to code protocols only when necessary. The adopted protocols include:
- Nuqtadan nuqtaga protokol (PPP)
- Internet standard protocol for transporting IP-diagrammalar over a point-to-point link.
- TCP / IP /UDP
- Foundation Protocols for TCP/IP protocol suite
- Object Exchange Protocol (OBEX)
- Session-layer protocol for the exchange of objects, providing a model for object and operation representation
- Wireless Application Environment/Wireless Application Protocol (WAE/WAP)
- WAE specifies an application framework for wireless devices and WAP is an open standard to provide mobile users access to telephony and information services.[112]
Baseband error correction
Depending on packet type, individual packets may be protected by xatolarni tuzatish, either 1/3 rate oldinga xatoni tuzatish (FEC) or 2/3 rate. In addition, packets with CRC will be retransmitted until acknowledged by avtomatik takroriy so'rov (ARQ).
Setting up connections
Any Bluetooth device in discoverable mode transmits the following information on demand:
- Device name
- Device class
- Xizmatlar ro'yxati
- Technical information (for example: device features, manufacturer, Bluetooth specification used, clock offset)
Any device may perform an inquiry to find other devices to connect to, and any device can be configured to respond to such inquiries. However, if the device trying to connect knows the address of the device, it always responds to direct connection requests and transmits the information shown in the list above if requested. Use of a device's services may require pairing or acceptance by its owner, but the connection itself can be initiated by any device and held until it goes out of range. Some devices can be connected to only one device at a time, and connecting to them prevents them from connecting to other devices and appearing in inquiries until they disconnect from the other device.
Every device has a unique 48-bit address. However, these addresses are generally not shown in inquiries. Instead, friendly Bluetooth names are used, which can be set by the user. This name appears when another user scans for devices and in lists of paired devices.
Most cellular phones have the Bluetooth name set to the manufacturer and model of the phone by default. Most cellular phones and laptops show only the Bluetooth names and special programs are required to get additional information about remote devices. This can be confusing as, for example, there could be several cellular phones in range named T610 (qarang Bluejacking ).
Pairing and bonding
Motivatsiya
Many services offered over Bluetooth can expose private data or let a connecting party control the Bluetooth device. Security reasons make it necessary to recognize specific devices, and thus enable control over which devices can connect to a given Bluetooth device. At the same time, it is useful for Bluetooth devices to be able to establish a connection without user intervention (for example, as soon as in range).
To resolve this conflict, Bluetooth uses a process called bog'lash, and a bond is generated through a process called pairing. The pairing process is triggered either by a specific request from a user to generate a bond (for example, the user explicitly requests to "Add a Bluetooth device"), or it is triggered automatically when connecting to a service where (for the first time) the identity of a device is required for security purposes. These two cases are referred to as dedicated bonding and general bonding respectively.
Pairing often involves some level of user interaction. This user interaction confirms the identity of the devices. When pairing completes, a bond forms between the two devices, enabling those two devices to connect in the future without repeating the pairing process to confirm device identities. When desired, the user can remove the bonding relationship.
Amalga oshirish
During pairing, the two devices establish a relationship by creating a umumiy sir sifatida tanilgan link key. If both devices store the same link key, they are said to be juftlashgan yoki bog'langan. A device that wants to communicate only with a bonded device can kriptografik jihatdan autentifikatsiya qilish the identity of the other device, ensuring it is the same device it previously paired with. Once a link key is generated, an authenticated Asynchronous Connection-Less (ACL) link between the devices may be shifrlangan to protect exchanged data against tinglash. Users can delete link keys from either device, which removes the bond between the devices—so it is possible for one device to have a stored link key for a device it is no longer paired with.
Bluetooth services generally require either encryption or authentication and as such require pairing before they let a remote device connect. Some services, such as the Object Push Profile, elect not to explicitly require authentication or encryption so that pairing does not interfere with the user experience associated with the service use-cases.
Pairing mechanisms
Pairing mechanisms changed significantly with the introduction of Secure Simple Pairing in Bluetooth v2.1. The following summarizes the pairing mechanisms:
- Legacy pairing: This is the only method available in Bluetooth v2.0 and before. Each device must enter a PIN-kod; pairing is only successful if both devices enter the same PIN code. Any 16-byte UTF-8 string may be used as a PIN code; however, not all devices may be capable of entering all possible PIN codes.
- Limited input devices: The obvious example of this class of device is a Bluetooth Hands-free headset, which generally have few inputs. These devices usually have a fixed PIN, for example "0000" or "1234", that are hard-coded into the device.
- Numeric input devices: Mobile phones are classic examples of these devices. They allow a user to enter a numeric value up to 16 digits in length.
- Alpha-numeric input devices: PCs and smartphones are examples of these devices. They allow a user to enter full UTF-8 text as a PIN code. If pairing with a less capable device the user must be aware of the input limitations on the other device; there is no mechanism available for a capable device to determine how it should limit the available input a user may use.
- Secure Simple Pairing (SSP): This is required by Bluetooth v2.1, although a Bluetooth v2.1 device may only use legacy pairing to interoperate with a v2.0 or earlier device. Secure Simple Pairing uses a form of public key cryptography, and some types can help protect against man in the middle, or MITM attacks. SSP has the following authentication mechanisms:
- Just works: As the name implies, this method just works, with no user interaction. However, a device may prompt the user to confirm the pairing process. This method is typically used by headsets with minimal IO capabilities, and is more secure than the fixed PIN mechanism this limited set of devices uses for legacy pairing. This method provides no man-in-the-middle (MITM) protection.
- Numeric comparison: If both devices have a display, and at least one can accept a binary yes/no user input, they may use Numeric Comparison. This method displays a 6-digit numeric code on each device. The user should compare the numbers to ensure they are identical. If the comparison succeeds, the user(s) should confirm pairing on the device(s) that can accept an input. This method provides MITM protection, assuming the user confirms on both devices and actually performs the comparison properly.
- Passkey Entry: This method may be used between a device with a display and a device with numeric keypad entry (such as a keyboard), or two devices with numeric keypad entry. In the first case, the display presents a 6-digit numeric code to the user, who then enters the code on the keypad. In the second case, the user of each device enters the same 6-digit number. Both of these cases provide MITM protection.
- Out of band (OOB): This method uses an external means of communication, such as yaqin atrofdagi aloqa (NFC) to exchange some information used in the pairing process. Pairing is completed using the Bluetooth radio, but requires information from the OOB mechanism. This provides only the level of MITM protection that is present in the OOB mechanism.
SSP is considered simple for the following reasons:
- In most cases, it does not require a user to generate a passkey.
- For use cases not requiring MITM protection, user interaction can be eliminated.
- Uchun numeric comparison, MITM protection can be achieved with a simple equality comparison by the user.
- Using OOB with NFC enables pairing when devices simply get close, rather than requiring a lengthy discovery process.
Xavfsizlik masalalari
Prior to Bluetooth v2.1, encryption is not required and can be turned off at any time. Moreover, the encryption key is only good for approximately 23.5 hours; using a single encryption key longer than this time allows simple XOR attacks to retrieve the encryption key.
- Turning off encryption is required for several normal operations, so it is problematic to detect if encryption is disabled for a valid reason or a security attack.
Bluetooth v2.1 addresses this in the following ways:
- Encryption is required for all non-SDP (Service Discovery Protocol) connections
- A new Encryption Pause and Resume feature is used for all normal operations that require that encryption be disabled. This enables easy identification of normal operation from security attacks.
- The encryption key must be refreshed before it expires.
Link keys may be stored on the device file system, not on the Bluetooth chip itself. Many Bluetooth chip manufacturers let link keys be stored on the device—however, if the device is removable, this means that the link key moves with the device.
Xavfsizlik
Umumiy nuqtai
Bluetooth implements maxfiylik, autentifikatsiya va kalit derivation with custom algorithms based on the XAVFSIZLIK + blok shifr. Bluetooth key generation is generally based on a Bluetooth PIN, which must be entered into both devices. This procedure might be modified if one of the devices has a fixed PIN (e.g., for headsets or similar devices with a restricted user interface). During pairing, an initialization key or master key is generated, using the E22 algorithm.[113]The E0 stream cipher is used for encrypting packets, granting confidentiality, and is based on a shared cryptographic secret, namely a previously generated link key or master key. Those keys, used for subsequent encryption of data sent via the air interface, rely on the Bluetooth PIN, which has been entered into one or both devices.
An overview of Bluetooth vulnerabilities exploits was published in 2007 by Andreas Becker.[114]
In September 2008, the Milliy standartlar va texnologiyalar instituti (NIST) published a Guide to Bluetooth Security as a reference for organizations. It describes Bluetooth security capabilities and how to secure Bluetooth technologies effectively. While Bluetooth has its benefits, it is susceptible to denial-of-service attacks, eavesdropping, man-in-the-middle attacks, message modification, and resource misappropriation. Users and organizations must evaluate their acceptable level of risk and incorporate security into the lifecycle of Bluetooth devices. To help mitigate risks, included in the NIST document are security checklists with guidelines and recommendations for creating and maintaining secure Bluetooth piconets, headsets, and smart card readers.[115]
Bluetooth v2.1 – finalized in 2007 with consumer devices first appearing in 2009 – makes significant changes to Bluetooth's security, including pairing. Ga qarang pairing mechanisms section for more about these changes.
Bluejacking
Bluejacking is the sending of either a picture or a message from one user to an unsuspecting user through Bluetooth wireless technology. Common applications include short messages, e.g., "You've just been bluejacked!"[116] Bluejacking does not involve the removal or alteration of any data from the device.[117] Bluejacking can also involve taking control of a mobile device wirelessly and phoning a premium rate line, owned by the bluejacker. Security advances have alleviated this issue[iqtibos kerak ].
History of security concerns
2001–2004
In 2001, Jakobsson and Wetzel from Qo'ng'iroq laboratoriyalari discovered flaws in the Bluetooth pairing protocol and also pointed to vulnerabilities in the encryption scheme.[118] In 2003, Ben and Adam Laurie from A.L. Digital Ltd. discovered that serious flaws in some poor implementations of Bluetooth security may lead to disclosure of personal data.[119] In a subsequent experiment, Martin Herfurt from the trifinite.group was able to do a field-trial at the CeBIT fairgrounds, showing the importance of the problem to the world. A new attack called BlueBug was used for this experiment.[120] In 2004 the first purported virus using Bluetooth to spread itself among mobile phones appeared on the Symbian OS.[121]The virus was first described by Kasperskiy laboratoriyasi and requires users to confirm the installation of unknown software before it can propagate. The virus was written as a proof-of-concept by a group of virus writers known as "29A" and sent to anti-virus groups. Thus, it should be regarded as a potential (but not real) security threat to Bluetooth technology or Symbian OS since the virus has never spread outside of this system. In August 2004, a world-record-setting experiment (see also Bluetooth sniping ) showed that the range of Class 2 Bluetooth radios could be extended to 1.78 km (1.11 mi) with directional antennas and signal amplifiers.[122]This poses a potential security threat because it enables attackers to access vulnerable Bluetooth devices from a distance beyond expectation. The attacker must also be able to receive information from the victim to set up a connection. No attack can be made against a Bluetooth device unless the attacker knows its Bluetooth address and which channels to transmit on, although these can be deduced within a few minutes if the device is in use.[123]
2005
In January 2005, a mobile zararli dastur worm known as Lasco surfaced. The worm began targeting mobile phones using Symbian OS (Series 60 platformasi ) using Bluetooth enabled devices to replicate itself and spread to other devices. The worm is self-installing and begins once the mobile user approves the transfer of the file (Velasco.sis) from another device. Once installed, the worm begins looking for other Bluetooth enabled devices to infect. Additionally, the worm infects other .SIS files on the device, allowing replication to another device through the use of removable media (Secure Digital, CompactFlash, va boshqalar.). The worm can render the mobile device unstable.[124]
2005 yil aprel oyida, Kembrij universiteti security researchers published results of their actual implementation of passive attacks against the PIN-based pairing between commercial Bluetooth devices. They confirmed that attacks are practicably fast, and the Bluetooth symmetric key establishment method is vulnerable. To rectify this vulnerability, they designed an implementation that showed that stronger, asymmetric key establishment is feasible for certain classes of devices, such as mobile phones.[125]
In June 2005, Yaniv Shaked[126] and Avishai Wool[127] published a paper describing both passive and active methods for obtaining the PIN for a Bluetooth link. The passive attack allows a suitably equipped attacker to eavesdrop on communications and spoof if the attacker was present at the time of initial pairing. The active method makes use of a specially constructed message that must be inserted at a specific point in the protocol, to make the master and slave repeat the pairing process. After that, the first method can be used to crack the PIN. This attack's major weakness is that it requires the user of the devices under attack to re-enter the PIN during the attack when the device prompts them to. Also, this active attack probably requires custom hardware, since most commercially available Bluetooth devices are not capable of the timing necessary.[128]
In August 2005, police in Kambridjeshire, England, issued warnings about thieves using Bluetooth enabled phones to track other devices left in cars. Police are advising users to ensure that any mobile networking connections are de-activated if laptops and other devices are left in this way.[129]
2006
In April 2006, researchers from Secure Network va F-xavfsiz published a report that warns of the large number of devices left in a visible state, and issued statistics on the spread of various Bluetooth services and the ease of spread of an eventual Bluetooth worm.[130]
In October 2006, at the Luxemburgish Hack.lu Security Conference, Kevin Finistere and Thierry Zoller demonstrated and released a remote root shell via Bluetooth on Mac OS X v10.3.9 and v10.4. They also demonstrated the first Bluetooth PIN and Linkkeys cracker, which is based on the research of Wool and Shaked.[131]
2017
In April 2017, security researchers at Armis discovered multiple exploits in the Bluetooth software in various platforms, including Microsoft Windows, Linux, Olma iOS va Google Android. These vulnerabilities are collectively called "BlueBorne ". The exploits allow an attacker to connect to devices or systems without authentication and can give them "virtually full control over the device". Armis contacted Google, Microsoft, Apple, Samsung and Linux developers allowing them to patch their software before the coordinated announcement of the vulnerabilities on 12 September 2017.[132]
2018
In July 2018, researchers at the Technion – Israel Institute of Technology identified a security vulnerability in the latest Bluetooth pairing procedures: Secure Simple Pairing and LE Secure Connections.[133][134]
2019
In August 2019, security researchers at the Singapore University of Technology and Design, Helmholtz Center for Information Security, and University of Oxford discovered a vulnerability in the key negotiation that would "brute force the negotiated encryption keys, decrypt the eavesdropped ciphertext, and inject valid encrypted messages (in real-time).".[135][136]
Sog'liqni saqlash muammolari
Bluetooth uses the radio chastotasi spectrum in the 2.402 GHz to 2.480 GHz range,[137] which is non-ionizing radiation, of similar bandwidth to the one used by wireless and mobile phones. No specific demonstration of harm has been demonstrated up to date, even if wireless transmission has been included by IARC in the possible kanserogen ro'yxat. Maximum power output from a Bluetooth radio is 100 mVt for class 1, 2.5 mW for class 2, and 1 mW for class 3 devices. Even the maximum power output of class 1 is a lower level than the lowest-powered mobile phones.[138] UMTS va W-CDMA output 250 mW, GSM1800/1900 outputs 1000 mW, and GSM850/900 outputs 2000 mW.
Mukofotlash dasturlari
The Bluetooth Innovation World Cup, a marketing initiative of the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG), was an international competition that encouraged the development of innovations for applications leveraging Bluetooth technology in sports, fitness and health care products. The competition aimed to stimulate new markets.[139]
The Bluetooth Innovation World Cup morphed into the Bluetooth Breakthrough Awards in 2013. Bluetooth SIG subsequently launched the Imagine Blue Award in 2016 at Bluetooth World.[140] The Breakthrough Awards[141] Bluetooth program highlights the most innovative products and applications available today, prototypes coming soon, and student-led projects in the making.
Shuningdek qarang
- ANT +
- Bluetooth to'plami – building blocks that make up the various implementations of the Bluetooth protocol.
- Bluetooth profili – features used within the bluetooth stack
- Ko'krak otish
- BlueSoleil – proprietary Bluetooth driver.
- Bluetooth Low Energy Beacons (AltBeacon, iBeacon, Eddystone )
- Bluetooth Mesh
- Continua sog'liqni saqlash alyansi
- DASH7
- Eshitish vositasi (audio)
- Hotspot (Wi-Fi)
- Bluetooth uchun Java API-lari
- Kalit topuvchi
- Li-Fi
- MyriaNed
- Dala yaqinidagi aloqa
- RuBee – secure wireless protocol alternative.
- Bog'lanish
- Mavzu (tarmoq protokoli)
- Wi-Fi HaLow
- ZigBee – low-power lightweight wireless protocol in the ISM guruhi.
Izohlar
- ^ Many operating systems delete incomplete files if the file transfer has failed.
Adabiyotlar
- ^ a b bluAir. "Bluetooth Range: 100m, 1km, or 10km?". bluair.pl. Olingan 4 iyun 2015.
- ^ a b v d "Basics | Bluetooth Technology Website". Bluetooth.com. 23 may 2010 yil.
- ^ "About us - Bluetooth Technology Website". Bluetooth.com. Olingan 8 may 2019.
- ^ "Brand Enforcement Program". Bluetooth.com. Olingan 8 may 2019.
- ^ a b Happich, Julien (24 February 2010). "Global shipments of short range wireless ICs to exceed 2 billion units in 2010". EE Times. Olingan 25 oktyabr 2019.
- ^ "'So, that's why it's called Bluetooth!' and other surprising tech name origins". PCWorld. Olingan 16 avgust 2017.
- ^ Kardach, Jim (5 March 2008). "Tech History: How Bluetooth got its name". eetimes. Olingan 11 iyun 2013.
- ^ Forsit, Mark (2011). The Etymologicon. London: Icon Books Ltd. p.139.
- ^ "Bluetooth-ning muhim bosqichlari". Ericsson Technology Licensing. 22 mart 2004 yil. Arxivlangan asl nusxasi 2004 yil 20 iyunda.
- ^ "Bluetooth on Twitter".
- ^ "Bluetooth Experience Icons" (PDF). Bluetooth maxsus foizlar guruhi. Olingan 21 oktyabr 2016.
Bluetooth Experience Icons borrow two of these three features: the blue color and the rune-inspired symbol.
- ^ "The Bluetooth". Axborot asri. 24 May 2001. Arxivlangan asl nusxasi 2007 yil 22 dekabrda. Olingan 1 fevral 2008.
- ^ Nguyen, Tuan C. "Who Invented Bluetooth?". ThoughtCo. Olingan 11 oktyabr 2019.
- ^ "Grattis Bluetooth, 10 år". etn.se. Olingan 29 oktyabr 2019.
- ^ "Sveriges 20 främsta innovationer de senaste 35 åren". Veckans affärer. Olingan 29 oktyabr 2019.
- ^ "122 Nobel prize candidates" (PDF).
- ^ "De största innovationerna i modern tid". innovatorsradet.se. Arxivlandi asl nusxasi 2019 yil 17-may kuni. Olingan 29 oktyabr 2019.
- ^ a b "Bluetooth Radio Interface, Modulation & Channels". Radio-Electronics.com.
- ^ Bluetooth Specification Version 5.0 (PDF download). Bluetooth Special Interest Group. Olingan Bluetooth Core Specifications, 1 December 2017. Page 2535.
- ^ Kurawar, Arwa; Koul, Ayushi; Patil, Viki Tukaram (August 2014). "Survey of Bluetooth and Applications". International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Engineering & Technology. 3: 2832–2837. ISSN 2278-1323.
- ^ "How Bluetooth Technology Works". Bluetooth SIG. Arxivlandi asl nusxasi on 17 January 2008. Olingan 1 fevral 2008.
- ^ Newton, Harold. (2007). Newton’s telecom dictionary. New York: Flatiron Publishing.
- ^ "Class 1 Bluetooth Dongle Test". Amperordirect.com. Olingan 4 sentyabr 2010.
- ^ "WT41 Long Range Bluetooth Module".
- ^ "BluBear Industrial Long Range Bluetooth 2.1 Module with EDR". Arxivlandi asl nusxasi 2013 yil 17-iyulda.
- ^ "OEM Bluetooth Serial Port Module OBS433".
- ^ "Traditional Profile Specifications". Bluetooth.com. Olingan 28 oktyabr 2019.
- ^ Ian, Paul. "Wi-Fi Direct vs. Bluetooth 4.0: A Battle for Supremacy". Kompyuter dunyosi. Olingan 27 dekabr 2013.
- ^ "History of the Bluetooth Special Interest Group". Bluetooth.com.
- ^ Sauter, Martin (2 August 2017). From GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile Broadband. John Wiley & Sons. p. 491. ISBN 978-1-119-34690-6.
- ^ Penttinen, Jyrki T. J. (16 March 2015). The Telecommunications Handbook: Engineering Guidelines for Fixed, Mobile and Satellite Systems. John Wiley & Sons. p. 129. ISBN 978-1-119-94488-1.
- ^ "Portable Wireless Bluetooth Compatible Speakers". Trusound Audio. Arxivlandi asl nusxasi 2016 yil 18 aprelda. Olingan 7 aprel 2016.
- ^ "Bluetooth Revisited". www.techpayout.com. 2014 yil 27 mart. Olingan 10 may 2016.
- ^ "Bluetooth Technology". mobileinfo.com.
- ^ "Samsung Omnia II: Fayllarni Bluetooth FTP bilan qanday o'tkazish mumkin". 11 December 2009.
- ^ Jon Fuller. "How Bluetooth Surveillance Works". howstuffworks. Olingan 26 may 2015.
- ^ "Wii Controller". Bluetooth SIG. Arxivlandi asl nusxasi 2008 yil 20 fevralda. Olingan 1 fevral 2008.
- ^ "Telemedicine.jp". Telemedicine.jp. Olingan 4 sentyabr 2010.
- ^ "Tai nghe bluetooth nokia". tainghebluetooth.com.
- ^ "Real Time Location Systems" (PDF). klarinoks. Olingan 4 avgust 2010.
- ^ "Tenbu's nio Is Kind of Like a Car Alarm for Your Cellphone". OhGizmo!. Olingan 4 iyun 2015.
- ^ "Wireless waves used to track travel times". CTV Calgary News. 2012 yil 26-noyabr. Olingan 11 iyul 2013.
- ^ "Wireless Data and Power Transfer of an Optogenetic Implantable Visual Cortex Stimulator (PDF Download Available)". ResearchGate. Olingan 20 sentyabr 2017.
- ^ www.digitaltrends.com https://www.digitaltrends.com/computing/what-is-wi-fi-direct/. Olingan 7 sentyabr 2020. Yo'qolgan yoki bo'sh
sarlavha =(Yordam bering) - ^ Mroz, Mandy (21 May 2018). "Bluetooth hearing aids: Hearing aids with Bluetooth technology use today's wireless technology to help you easily stay connected to iOS and Android phones, televisions, tablets and other favorite audio devices". Sog'lom eshitish. Olingan 15 iyul 2018.
- ^ "Tomosha qiling". Bluetooth.com. Arxivlandi asl nusxasi 2010 yil 18 sentyabrda. Olingan 4 sentyabr 2010.
- ^ Eizikowitz, Grant (5 March 2018). "Why does Bluetooth still suck?". Business Insider. Olingan 15 iyul 2018.
- ^ a b "How Bluetooth Works". How Stuff Works. 2010 yil 30 iyun.
- ^ "Specification Documents". Bluetooth.com. 2010 yil 30 iyun.
- ^ "Bluetooth for Programmers" (PDF). MIT Computer Science And Artificial Intelligence Laboratory.
- ^ a b v d "Bluetooth Wireless Technology FAQ – 2010". Olingan 4 sentyabr 2010.
- ^ "Network Protection Technologie". Changes to Functionality in Microsoft Windows XP Service Pack 2. Microsoft Technet. Arxivlandi asl nusxasi on 1 January 2008. Olingan 1 fevral 2008.
- ^ "Apple Introduces "Jaguar," the Next Major Release of Mac OS X" (Matbuot xabari). Olma. 17 Iyul 2002. Arxivlangan asl nusxasi 2008 yil 18 fevralda. Olingan 4 fevral 2008.
- ^ "Official Linux Bluetooth protocol stack". BlueZ. Olingan 4 sentyabr 2010.
- ^ "Bluedroid stack in android". Jacob su. Olingan 19 iyun 2019.
- ^ "Affix Bluetooth Protocol Stack for Linux". Affiks. Olingan 19 iyun 2019.
- ^ Maksim Yevmenkin (2002). "ng_bluetooth.4 — placeholder for global Bluetooth variables". BSD o'zaro faoliyat ma'lumotnomasi. FreeBSD. Xulosa.
- ^ Iain Hibbert; Itronix Inc (2006). "bluetooth.4 — Bluetooth Protocol Family". BSD o'zaro faoliyat ma'lumotnomasi. NetBSD. Xulosa.
- ^ Ted Unangst (11 July 2014). "CVS: cvs.openbsd.org: src". source-changes@cvs (Pochta ro'yxati). OpenBSD.
bluetooth support doesn't work and isn't going anywhere.
- ^ tbert, ed. (2014 yil 29-iyul). "g2k14: Ted Unangst on the Art of the Tedu". OpenBSD jurnali.
Of these, you may possibly miss bluetooth support. Unfortunately, the current code doesn't work and isn't structured properly to encourage much future development.
- ^ Hasso Tepper, ed. (2008). "bluetooth.4 — Bluetooth Protocol Family". BSD o'zaro faoliyat ma'lumotnomasi. DragonFly BSD. Xulosa.
- ^ "sys/netgraph7/bluetooth/common/ng_bluetooth.c". BSD o'zaro faoliyat ma'lumotnomasi. DragonFly BSD.
- ^ Sascha Wildner (15 November 2014). "kernel/netgraph7: Port the kernel part of the netgraph7 bluetooth stack". DragonFly BSD.
- ^ "Bizning tariximiz". Bluetooth.com. Arxivlandi asl nusxasi 2018 yil 25-may kuni. Olingan 24 avgust 2018.
- ^ "English Introduction to Membership". Bluetooth.org. Arxivlandi asl nusxasi 2014 yil 26 iyunda. Olingan 13 may 2014.
- ^ "Compatibility guide" (PDF). 2016. Olingan 18 dekabr 2019.
- ^ IEEE Std 802.15.1–2002 – IEEE Standard for Information technology – Telecommunications and information exchange between systems – Local and metropolitan area networks – Specific requirements Part 15.1: Wireless Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications for Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPANs). 2002. doi:10.1109/IEEESTD.2002.93621. ISBN 978-0-7381-3335-5.
- ^ a b Guy Kewney (16 November 2004). "High speed Bluetooth comes a step closer: enhanced data rate approved". Newswireless.net. Olingan 4 fevral 2008.
- ^ IEEE Std 802.15.1-2005 - IEEE Axborot texnologiyalari standarti - Telekommunikatsiyalar va tizimlar o'rtasida axborot almashinuvi - Mahalliy va metropoliten tarmoqlari - Maxsus talablar 15.1-qism: Simsiz shaxsiy tarmoq tarmoqlari uchun simsiz o'rta kirishni boshqarish (MAC) va jismoniy qatlam (PHY) xususiyatlari.. doi:10.1109 / IEEESTD.2005.96290. ISBN 978-0-7381-4708-6.
- ^ a b v "Shartnoma hujjatlari". Bluetooth SIG. Olingan 3 may 2012.
- ^ "HTC TyTN spetsifikatsiyasi" (PDF). HTC. Arxivlandi asl nusxasi (PDF) 2006 yil 12 oktyabrda. Olingan 4 fevral 2008.
- ^ "Oddiy juft oq qog'oz" (PDF). V10r00 versiyasi. Bluetooth SIG. 3 Avgust 2006. Arxivlangan asl nusxasi (PDF) 2006 yil 18 oktyabrda. Olingan 1 fevral 2007.
- ^ "Bluetooth Core Version 3.0 + HS spetsifikatsiyasi".
- ^ "Bluetooth yadrosi spetsifikatsiyasi bo'yicha qo'shimcha (CSA) 1".
- ^ Devid Meyer (2009 yil 22-aprel). "Bluetooth 3.0 ultra polosasiz chiqarildi". zdnet.co.uk. Olingan 22 aprel 2009.
- ^ "Wimedia.org". Wimedia.org. 4 yanvar 2010. Arxivlangan asl nusxasi 2002 yil 26 aprelda. Olingan 4 sentyabr 2010.
- ^ "Wimedia.org". Arxivlandi asl nusxasi 2009 yil 23 martda. Olingan 4 sentyabr 2010.
- ^ "bluetooth.com". Olingan 29 yanvar 2015.
- ^ "USB.org". USB.org. 16 Mart 2009. Arxivlangan asl nusxasi 2011 yil 10 iyunda. Olingan 4 sentyabr 2010.
- ^ "Incisor.tv". Incisor.tv. 16 Mart 2009. Arxivlangan asl nusxasi 2018 yil 16 sentyabrda. Olingan 4 sentyabr 2010.
- ^ "Bluetooth guruhi ultra polosali tarmoqqa tushadi, ko'zlari 60 gigagerts". EETimes. Olingan 4 iyun 2015.
- ^ "Hisobot: 2013 yilgacha ultra keng tarmoqli o'ladi". EETimes. Olingan 4 iyun 2015.
- ^ "Simon Stenhouse - sulukga urinish" (PDF). incisor.tv. Arxivlandi asl nusxasi (PDF) 2015 yil 24 sentyabrda. Olingan 4 iyun 2015.
- ^ "Wibree forumi Bluetooth SIG bilan birlashadi" (PDF) (Matbuot xabari). Nokia. 12 Iyun 2007. Arxivlangan asl nusxasi (PDF) 2014 yil 29 dekabrda. Olingan 4 fevral 2008.
- ^ "Bluetooth.com". Bluetooth.com. Arxivlandi asl nusxasi 2009 yil 21 dekabrda. Olingan 4 sentyabr 2010.
- ^ "Bluetooth SIG Smart Marks-ni namoyish etadi, v4.0 mosligini keraksiz murakkabligi bilan izohlaydi". Engadget.
- ^ "Dialog yarim o'tkazgich".
- ^ "BlueNRG Bluetooth® past energiyali simsiz tarmoq protsessori - STMicroelectronics". st.com. Olingan 4 iyun 2015.
- ^ "::: 笙 科 電子 -Amiccom". Arxivlandi asl nusxasi 2013 yil 25-avgustda.
- ^ "CSR.com". KSS. Arxivlandi asl nusxasi 2012 yil 28 iyunda. Olingan 7 aprel 2011.
- ^ "Nordicsemi.com". Shimoliy yarim o'tkazgich. Arxivlandi asl nusxasi 2011 yil 2 aprelda. Olingan 7 aprel 2011.
- ^ "TI.com". Texas Instruments. Olingan 7 aprel 2011.
- ^ "iFixit MacBook Air 13" 2011 yil o'rtalarida Teardown ". iFixit.com. Olingan 27 iyul 2011.
- ^ "Broadcom.com - BCM20702 - Bluetooth past quvvatli (BLE) qo'llab-quvvatlaydigan yagona chipli Bluetooth® 4.0 HCI Qarori".. Broadcom. Arxivlandi asl nusxasi 2011 yil 11 avgustda. Olingan 27 iyul 2011.
- ^ "Press-relizlar tafsiloti | Bluetooth texnologiyasi veb-sayti". Bluetooth.com. 2013 yil 4-dekabr. Olingan 13 may 2014.
- ^ "Qabul qilingan spetsifikatsiya; Bluetooth texnologiyasi veb-sayti". Bluetooth.com. 2013 yil 4-dekabr. Olingan 14 may 2014.
- ^ "Redmondpie".
- ^ "DailyTech". Arxivlandi asl nusxasi 2014 yil 7 dekabrda.
- ^ "MWC 2017: Sony yangi 5G-darajali Xperia XZ seriyasini yuqori darajadagi kameraga ega". IBT. Olingan 3 oktyabr 2019.
- ^ "HomePod - texnik shartlar". olma. Olingan 29 yanvar 2018.
- ^ cnxsoft (2016 yil 10-iyun). "Bluetooth 5 Bluetooth 4.0 LE uzatmalarining tezligini ikki baravar, to'rt baravar ko'p va'da qiladi".
- ^ "Bluetooth 5 standarti IoT uchun diapazon, tezlik va quvvatni oshirishga imkon beradi".
- ^ "Bluetooth® 5 diapazoni to'rt barobarga ko'payadi, tezlikni ikki baravar oshiradi, ma'lumotlar uzatish imkoniyatlarini 800 foizga oshiradi - Bluetooth texnologiyalari veb-sayti". www.bluetooth.com. Arxivlandi asl nusxasi 2018 yil 9-dekabr kuni. Olingan 12 dekabr 2018.
- ^ ""Keyingi haftada Bluetooth 5 "spetsifikatsiyasi 4 barobar ko'proq va 2 baravar tezroq bo'ladi [Yangilandi].
- ^ "Bluetooth 5: bilishingiz kerak bo'lgan barcha narsalar".
- ^ "Bluetooth Core Specification v5.0" (PDF yuklab olish). www.bluetooth.org.
- ^ "Bluetooth Core Specification Version 5.2 Feature Overview". (PDF).
- ^ "Bluetooth-ning yangi versiyasi - bu sizning minigarniturangizni tuzatish uchun". Simli. ISSN 1059-1028. Olingan 3 fevral 2020.
- ^ Clover, Juli. "Bluetooth SIG" LE Audio "ni audio almashish, ma'lumotlarning kam sarflanishi, eshitish vositalarini qo'llab-quvvatlash va boshqa narsalar bilan e'lon qiladi". www.macrumors.com. Olingan 3 fevral 2020.
- ^ "Bluetooth LE yordamida eshitish vositalarini audio qo'llab-quvvatlash". Android Open Source loyihasi. Olingan 3 fevral 2020.
- ^ Veendrik, Garri J. M. (2017). Nanometr CMOS IClari: Asoslardan ASICgacha. Springer. p. 243. ISBN 9783319475974.
- ^ a b Stallings, Uilyam. (2005). Simsiz aloqa va tarmoqlar. '=' Yuqori Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall.
- ^ Juha T. Vainio (2000 yil 25-may). "Bluetooth xavfsizligi" (PDF). Xelsinki Texnologiya Universiteti. Olingan 1 yanvar 2009.
- ^ Andreas Beker (2007 yil 16-avgust). "Bluetooth Security & Hacks" (PDF). Ruhr-Universität Bochum. Olingan 10 oktyabr 2007.
- ^ Scarfone, K. & Padgette, J. (sentyabr 2008). "Bluetooth xavfsizligi bo'yicha qo'llanma" (PDF). Milliy standartlar va texnologiyalar instituti. Olingan 3 iyul 2013.
- ^ Jon Fuller. "Bluejacking nima?". howstuffworks. Olingan 26 may 2015.
- ^ Kaviarasu, S., & Mutupandian, P. (2016). Bluejacking texnologiyasi: sharh. Xalqaro trend tadqiqotlari va ishlanmalari jurnali, 3 (6), 1. Oktyabr 2018 yilda olingan https://www.researchgate.net/publication/314233155_Bluejacking_Technology_A_Review
- ^ "Bluetooth-ning xavfsizlik zaif tomonlari". RSA Xavfsizlik Konf. - Kriptografik trek. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.23.7357.
- ^ "Bluetooth". Bunker. Arxivlandi asl nusxasi 2007 yil 26-yanvarda. Olingan 1 fevral 2007.
- ^ "BlueBug". Trifinite.org. Olingan 1 fevral 2007.
- ^ Jon Oates (2004 yil 15-iyun). "Virus hujumlari mobil telefonlarga Bluetooth orqali". Ro'yxatdan o'tish. Olingan 1 fevral 2007.
- ^ "Uzoq masofadagi snarf". Trifinite.org. Olingan 1 fevral 2007.
- ^ "Umumiy Bluetooth noto'g'ri tushunchalarini yo'q qilish". SANS. Olingan 9 iyul 2014.
- ^ "F-Secure zararli dastur haqida ma'lumot sahifalari: Lasco.A". F-Secure.com. Arxivlandi asl nusxasi 2008 yil 17 mayda. Olingan 5 may 2008.
- ^ Ford-Long Vong; Frank Stajano; Jolyon Clulow (2005 yil aprel). "Bluetooth ulanish protokolini tuzatish" (PDF). Kembrij universiteti kompyuter laboratoriyasi. Arxivlandi asl nusxasi (PDF) 2007 yil 16 iyunda. Olingan 1 fevral 2007.
- ^ "Arxivlangan nusxa". Arxivlandi asl nusxasi 2007 yil 9-noyabrda. Olingan 6 noyabr 2007.CS1 maint: nom sifatida arxivlangan nusxa (havola)
- ^ "Avishai Wool - Awisשי volu". tau.ac.il. Olingan 4 iyun 2015.
- ^ Yaniv Shaked; Avishai Wool (2005 yil 2-may). "Bluetooth PIN kodini buzish". Tel-Aviv universiteti elektrotexnika tizimlari maktabi. Olingan 1 fevral 2007.
- ^ "Telefon garovgirlari izlash va topshiriqni o'g'irlashda". Kembrijdagi kechki yangiliklar. Arxivlandi asl nusxasi 2007 yil 17-iyulda. Olingan 4 fevral 2008.
- ^ "To'liq xavfsizlikda Bluetooth atrofida aylanish" (PDF). F-xavfsiz. May 2006. Arxivlangan asl nusxasi (PDF) 2006 yil 10 iyunda. Olingan 4 fevral 2008.
- ^ Finistere & Zoller. "Sizning barcha Bluetooth-laringiz biznikidir" (PDF). arxiv.hack.lu.
- ^ "Tadqiqot guruhining BlueBorne ma'lumotlari - Armis laboratoriyalari". armis. Olingan 20 sentyabr 2017.
- ^ Agar siz Bluetooth-ni buzishni xohlamasangiz, hozirda iPhone va Android-laringizni yangilang, Forbes, 2019 yil 24-iyul.
- ^ Bluetooth juftligini buzish - Ruxsat etilgan koordinatali noto'g'ri egri hujum. Lior Neumann, Eli Biham, Technion - Isroil Texnologiya Instituti.
- ^ Yangi muhim Bluetooth xavfsizligi muammosi millionlab qurilmalarni hujumga duchor qiladi, Forbes, 2019 yil 15-avgust.
- ^ KNOB buzilgan: Bluetooth BR / EDR-ning shifrlash kalitidagi muzokaralari natijasida past entropiyani ekspluatatsiya qilish, Daniele Antonioli, SUTD; Nils Ole Tippenhauer, CISPA; Kasper B. Rasmussen, Oksford universiteti, Usenix Security '19, Stanta Klara, 15 avgust 2019.
- ^ D. Xomiyen; M. Eftimakis (2010 yil 20 oktyabr). "Bluetooth qo'llanmasi". Arxivlandi asl nusxasi (PDF) 2016 yil 12-dekabrda. Olingan 11 dekabr 2009.
- ^ M. Xietanen; T. Alanko (2005 yil oktyabr). "Simsiz aloqa tizimlarining radiochastota maydonlari bilan bog'liq kasbiy ta'sir" (PDF). URSIning XXVIII Bosh Assambleyasi - Ishlar. Union Radio-Scientifique Internationale. Arxivlandi asl nusxasi (PDF) 2006 yil 6 oktyabrda. Olingan 19 aprel 2007.
- ^ "Bluetooth Innovation World Cup". Bluetooth.com. Olingan 4 sentyabr 2010.
- ^ "Bluetooth SIG Bluetooth World-da Imagine Blue mukofotlari g'oliblarini e'lon qiladi". Bluetooth.com. Olingan 29 mart 2017.[doimiy o'lik havola ]
- ^ "Bluetooth yutuqlari mukofotlari". bluetooth.org. Arxivlandi asl nusxasi 2015 yil 15-iyulda. Olingan 4 iyun 2015.
